NMR spectroscopy is a powerful tool for biologists interested in the structure dynamics and interactions of biological macromolecules. For the four common nuclei noted above the magnetic moments are.
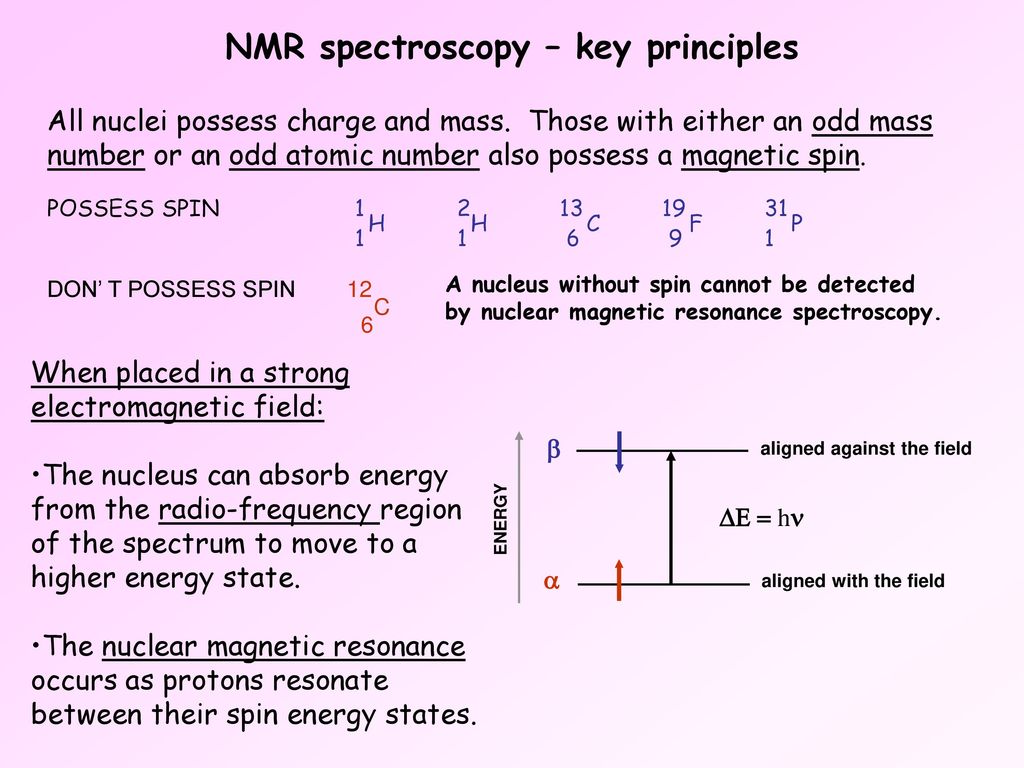
The nuclei of many elements such as 13 C spin generating a magnetic field.
. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy or NMR Spectroscopy can be used to identify any isotope unless the isotope has both an even number of protons and an even number of neutrons. Protein struc-ture determined by NMR spectroscopy. The WSU Center for NMR Spectroscopy is a central University facility that provides access to state-of-the-art NMR instrumentation.
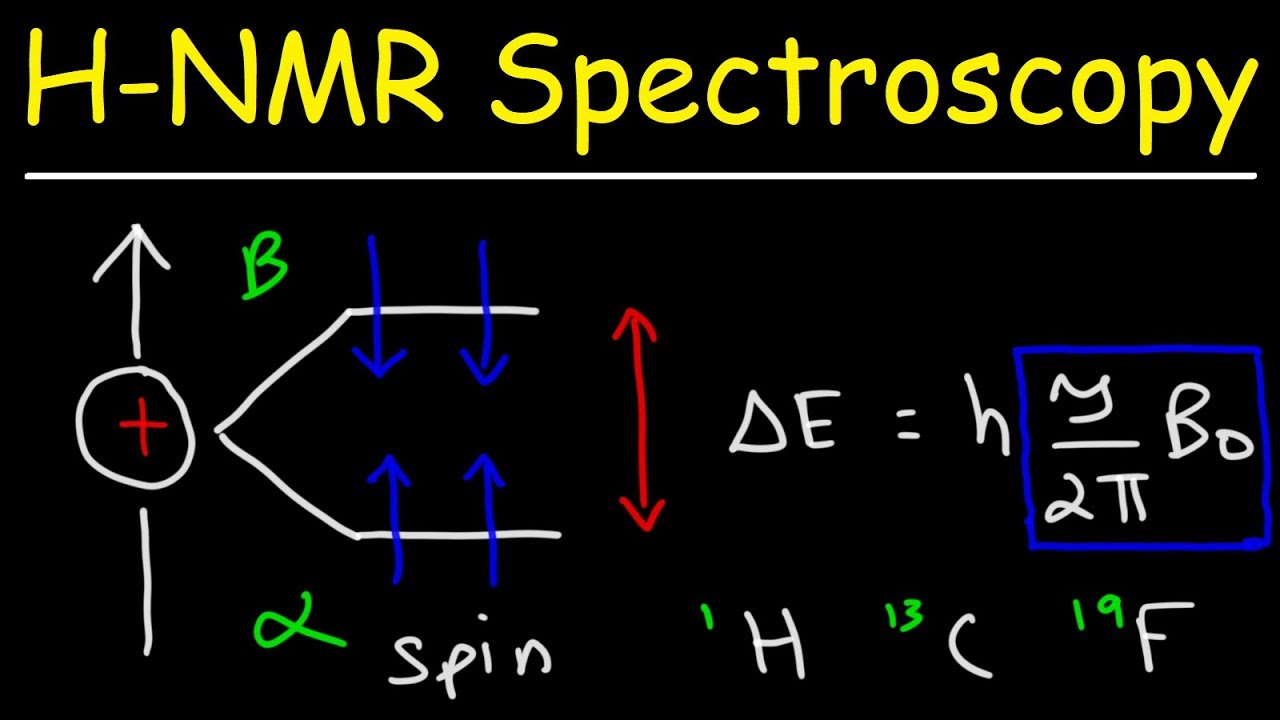
One is 12 which is anti-parallel to the magnetic field and the other is 12 which is parallel to the magnetic field. If an external magnetic field is applied an energy transfer is possible between the base energy to a higher energy level generally a single energy gap. Welcome to the WSU Center for NMR Spectroscopy To combat the spread of COVID-19 effective September 8 2021 there is a more stringent procedure for using the NMR lab.
Mass spectrometry MS is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ionsThe results are presented as a mass spectrum a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratioMass spectrometry is used in many different fields and is applied to pure samples as well. Metabonomic profiling of renal cell carcinoma. 2 Circular radiofrequency RF wave is polarized around the origin.
Copyright 1997-2019 JP. Progress in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy 79 2014 1447 23. This external energy applied to the molecule is absorbed and the.
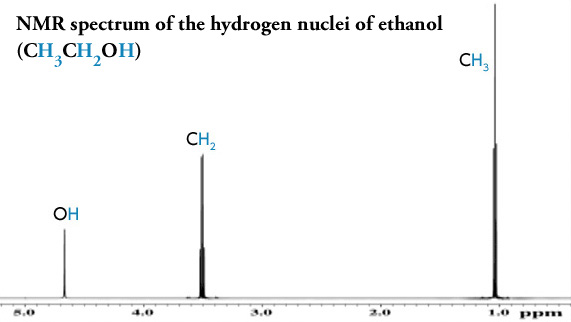
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance NMR Spectroscopy is a powerful analytical technique that can reveal structural information about many organic and inorganic molecules. 12 based on residual quadrupolar coupling of the form of Eq. 2 6 integral d 36 d 12 The relative area under the resonances at d 36 and 12 is 13 The integral is superimposed over the spectrum as a stair-step line.
1 H μ 27927 19 F μ 26273 31 P μ 11305 13 C μ 07022. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy or NMR Spectroscopy can be used to identify any isotope unless the isotope has both an even number of protons and an even number of neutrons. The height of each step is proportional to the area under the resonance.
NMR spectroscopy utilizes the absorption of electromagnetic radiation to flip the spin state of lower energy nuclei to higher energy states by applying radio waves along the x axis. It is important to remember that with NMR we are performing experiments on the nuclei of atoms not the electrons. In NMR magnetic nuclei of specific isotopes are aligned by a strong external magnet and then perturbed by a radio wave.
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy When a charged particle such as a proton spins on its axis it creates a magnetic field. Nuclear magnetic resonance NMR is a spec-. Hornak is Professor of Chemistry and Imaging Science at the Rochester Institute of Technology where he teaches courses in magnetic resonance imaging nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy analytical chemistry and physical chemistry.
On this page we will cover the basic theory behind the technique. Gao H Dong B Liu X Xuan H Huang Y Lin D. Nuclear magnetic resonance NMR spectroscopy explores the electronic environment of atoms.
H0 is magnetic field which separates the energy into two. However in the presence of a magnetic field B 0 they are oriented. 13 C Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Tutorial Key Concepts.
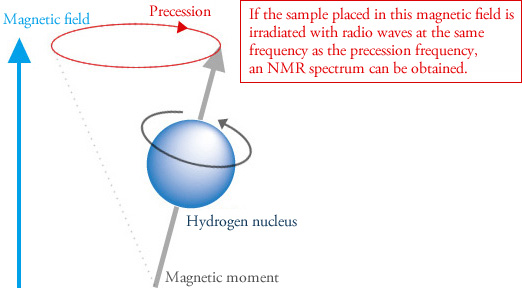
RF is applied to the x axis. As an introduction the history of NMR will highlight ho. Normally these tiny bar magnets are randomly oriented in space.
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance NMR Spectroscopy is a technique used for determining the structure of organic compounds. 1 H Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Tutorial Key Concepts. 22 Magnetic Resonance.
This review aims at presenting in an accessible manner the requirements and limitations of this technique. Some nuclei possess a magnetic moment - such as a hydrogen nucleus 1H or a carbon nucleus 13C. The following diagram gives the approximate frequencies that correspond to the spin state energy separations for each of these nuclei in an external magnetic field of 235 T.
The area under an NMR resonance is proportional to the number of nuclei that give rise to that resonance. For scientists to be able to measure the exact structure of compounds to understand their properties is key. High-resolution proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of human serum with multivariate data analysis.
Nuclear magnetic resonance NMR spectroscopy measurements have been firmly established among techniques used for obtaining valuable information about chemical and physical properties in a wide variety of scientific fields from biology and medicine to chemistry and physics. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy tutorial. A powerful technique useful for identifying the small to the very large When some atoms are placed in a strong magnetic field their nuclei behave.
E2 12 γh 2Π H0. The nuclei of many elements such as 1 H spin generating a magnetic field. INTRODUCTION TO NMR SPECTROSCOPY 11 Introduction Figure 11.
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy tutorial all along with the key concepts of Basic Principle of NMR The Source of NMR Spectra NMR spectrum Pattern of the Spectrum The. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance spectroscopy is a powerful and theoretically complex analytical tool. Thus the nucleus can be considered to be a tiny bar magnet.
Full solution of the evolution equations In this section we provide the complete solution of the evolu- tion equation Eq. These moments are in nuclear magnetons which are 50507810-27 JT-1. Four struc-tures of a 130 residue pro-tein derived from NMR constraints are overlaid to highlight the accuracy of structure determination by NMR spectroscopy.
Welcome to the WSU Center for NMR Spectroscopy To combat the spread of COVID-19 effective September 8 2021 there is a more stringent procedure for using the NMR lab. The chemical environment of specific nuclei is deduced from information obtained. 11 and a fluctuating quadrupolar interaction of the.
There are two major relaxation processes. Principle of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance NMR Spectroscopy The principle behind NMR is that many nuclei have spin and all nuclei are electrically charged.
Nmr Spectroscopy Key Principles Ppt Download

Analytical Chemistry A Guide To Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Nmr Compound Interest

Basic Introduction To Nmr Spectroscopy Youtube

Nmr Spectroscopy In Easy Way Part 1 Youtube

Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy

Nmr Spectroscopy Basic Theory Youtube
Nmr Basic Knowledge Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectrometer Nmr Products Jeol
Nmr Basic Knowledge Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectrometer Nmr Products Jeol

0 comments
Post a Comment